Who know how many trillions of dollars have been spent globally just on TELESCOPES ALONE? Not to mention all the other space vehicles, stations, launch pads, crews, maintenance, staff, experiments, training programs, etc. I don’t think there is any OVERSIGHT over all of this nonsense. I don’t even think there is any one group who really has a complete picture of all the “SPACE” Projects and their related expenses, or the reason for their existence and whether or not there is any real justification for them.
I KNOW for a fact that ALL of this is useless, and a waste of time and money. We will never really know what they are doing with all this, but I have a very strong sense that they are using it for our destruction whether intentionally or unintentionally.
They are using SMOKE and MIRRORS from above and below to deceive us. I know that most people would find that hard to believe. It is never the less the truth. There are so many aspects to their activities that no one person could follow it all or comprehend it all. I am not a rocket scientist or a physicist thank GOD. But, it does not take a college degree to discern what is happening. Afterall, in the final analysis all of it has a spiritual root. Spiritual things are discerned spiritually. All one needs is the Holy Spirit to uncover ALL TRUTH.
Scientists just love to play. They are maniacs driven to push the envelope farther and farther with no concern for the dangers. They are also driven to raise money. They have to keep justifying their existence. So they sell the investors and the public all on kinds of BULLSHIT reasons why we need to pay for what they are doing. They are filling our skies with all manner of energy and playing around with it to create their desired effects. They think they are in control. THEY ARE WRONG on TWO COUNTS. One, they have no idea what will happen when the experiment. They don’t really care what kind of repercussions or side effects they are creating. and the TRUTH is that GOD is in CONTROL. HE WILL put an end to this madness. In the meantime, he protects those who belong to HIM.
La Palma Gateway to the ASTRO WORLD
Waves, Rays and Energy Beams what are they really Up To?
Arecibo – FAST – DECEPTION
Magic Sword of the Elite
La Palma Gateway to the ASTRO WORLD
THE JANUS KEY
I like Dreamin
Image- Probably the most important word in your life! Part 1 – How Photography Changed Our World
Image – Probably the most important word in your life! Part 2 – What Do You Imagine?
IMAGE – Probably the most Important word in your life! Part 3 – THE BATTLE FOR YOUR MIND
spacer
REMEMBER FOLKS, IT IS ALL DONE WITH MIRRORS!
spacer
 |
spacer

It’s all starting to make sense…
I knew that X looked suspicious…
Think mirror… |
spacer
spacer
Why NASA’s Next Telescope Will Be Even Better Than James Webb | Unveiled

248K subscribers
Joan Gordon and Rachael Beaton In coordination with the science conference “Roman Science Inspired by Emerging JWST Results,” two guest speakers will present the history and science of the Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope. Joan Gordon, Ph.D., will provide insights into the remarkable life of the Nancy Grace Roman, the Roman mission’s namesake and NASA’s first chief of astronomy who is also known as “The Mother of Hubble.” Dr. Rachael Beaton of the Space Telescope Science Institute will follow with a discussion about the Roman Space Telescope mission, detailing how this wide-field and high-resolution observatory will achieve breakthrough science. Host: Brandon Lawton, STScI Recorded live on Thursday, June 22, 2023 More information: www.stsci.edu/public-lectures
1.08M subscribers
|
1:14] And God said, “Let there be lights in the dome of the sky to separate the day from the night; and let them be for signs and for seasons and for days and years, |
1.69M subscribers
Get 20% off a premium subscription to Brilliant at http://www.brilliant.org/answerswithjoe In the next decade, a handful of new mega telescopes, both space-based and ground-based, are poised to answer some of the biggest questions in science. My video on the James Webb Space Telescope: ![]() • The James Webb Sp… Support me on Patreon! http://www.patreon.com/answerswithjoe Get cool nerdy t-shirts at http://www.answerswithjoe.com/shirts Interested in getting a Tesla? Use my referral link and get discounts and perks: https://ts.la/joe74700 Become a channel member and get access to exclusive livestreams and content here:
• The James Webb Sp… Support me on Patreon! http://www.patreon.com/answerswithjoe Get cool nerdy t-shirts at http://www.answerswithjoe.com/shirts Interested in getting a Tesla? Use my referral link and get discounts and perks: https://ts.la/joe74700 Become a channel member and get access to exclusive livestreams and content here: ![]() / @joescott
/ @joescott
Minute 2:56 I wasn’t the telescopes that make the images from space possible. It is the SOPHISTICATED DATA TECHIQUE. They used to use artists to create rendition of what they imagined space to be. Now they use computers/AI to create the images. Supposedly by take bits of data from all the devices they have in space and creating the artistic computerized rendition.
SPACER
 James Webb Space Telescope
James Webb Space TelescopeThe successor to Hubble, the James Webb will feature a 6.4 meter mirror, dwarfing the 2 meter mirror on Hubble. It will focus on the infrared spectrum and will see further into the past than ever before. It’s currently scheduled to launch in 2021, but has been delayed multiple times.
JWST is performing ‘phenomenally’ one year on, say scientists, 25 Dec 2022. A year after its launch, astronomers are revealing the secrets of the universe, as the first scientific results from observations made by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) are released. This month, Physics World is publishing a series of blog posts on the discoveries. This is the fourth post in the series – you can read the previous one here.
The Surname Webb
Webb – The origin of the Webb surname is English and Scottish. It is believed to be occupational, deriving from the Middle English ‘webbe/webba’ (weaver), as seen in the Canterbury Tales. The surname Webb would be given to those who worked with and wove cloth, and their descendants.
JAMES
It means “supplanter” or “replacer. and derives from the Hebrew Jacob. Throughout history, James has been given to kings, presidents, entertainers, and regular folks alike
SUPPLANT
supplant | Etymology, origin and meaning
Online Etymology Dictionary
Dec 6, 2016 — SUPPLANT Meaning: “to trip up, overthrow, defeat, dispossess
Supplant Definition & Meaning
Dictionary.com
to take the place of (another), as through force, scheming, strategy, or the like. to replace (one thing) by something else.
WEBB
Webb Etymology – wiktionary
From Proto-Germanic*wabją (whence also Old High Germanweppi, Old Norsevefr), ultimately from Proto-Indo-European *webʰ-(“weave”). The Indo-European root is also the source of wasp, due to the insect’s woven nests.
Etymology of the name Webb; What does it REVEAL?
The surname Webb is derived from the Old English word “webba,” meaning “weaver.”
The surname Webb carries symbolic significance related to creativity, ingenuity, and skill. The spider’s web, which is often used as a symbol for the name, represents the intricate craftsmanshiprequired to create woven textiles. It also symbolizes strength and adaptability, as spider webs are known for their resilience and ability to adapt to changing environments.
Furthermore, the name Webb is associated with the concept of interconnectedness. (as in the World Wide WEB; and the One World Government)Just as a spider’s web is made up of interconnected strands, the name Webb suggests a connection between individuals and communities. This symbolism is particularly relevant in today’s globalized world, where people from different backgrounds and cultures are increasingly interconnected.
Another interpretation of the symbolism behind the name Webb is related to the idea of fate or destiny. In some cultures, spiders are seen as creatures that weave the fabric of fate, and the name Webb may therefore suggest a connection to the forces that shape (or control) our lives.This interpretation highlights the idea that our actions and choices are interconnected and can have far-reaching consequences.
 WFIRST – Wide-Field Infrared Survey Telescope or WFIRST/ The Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope (shortened as Roman or the Roman Space Telescope,
WFIRST – Wide-Field Infrared Survey Telescope or WFIRST/ The Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope (shortened as Roman or the Roman Space Telescope,
The Wide Field Infra Red Survey Telescope will have the same resolution as Hubble, but will be able to image 100x more of the sky at once. The plan was to use it in conjunction with the James Webb to find interesting targets. It is in danger of being cancelled later this year. The Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope / NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory (.gov) The Wide Field Infrared Survey Telescope (WFIRST) is a NASA observatory designed to perform Wide Field imaging and surveys of the near infrared (NIR) sky.
Nancy
nancy | Etymology, origin and meaning of the name
Online Etymology Dictionary
Apr 11, 2019 — proper name, mid-12c., from Old French Agnes,from Greek Hagnē “pure, chaste,” fem. of hagnos “holy, sacred” (of places); “chaste, pure; …
Agnus
Agnes – origin, meaning, popularity, and related names
Mom.com
From Greek, meaning “pure, holy”. The Latin cognate, agnus, means “lamb”. French forms are Agnès and Ines. Scandinavian forms are Agneta, Agnetha (Swedish),
Hagi
Hagia Definition & Meaning
Merriam-Webster
The meaning of HAGIA is consecrated eucharistic elementsin the Eastern Church.
Grace
grace (n.)
late 12c., “God’s unmerited favor, love, or help,” from Old French grace “pardon, divine grace, mercy; favor, thanks; elegance, virtue” (12c., Modern French grâce), from Latin gratia “favor, esteem, regard; pleasing quality, good will, gratitude”(source of Italian grazia, Spanish gracia; in Church use translating Greek kharisma), from gratus “pleasing, agreeable” (from PIE *gwreto-, suffixed form of root *gwere- (2) “to favor”).
Roman
Roman
noun and adjective, Old English, “of or pertaining to ancient Rome; an inhabitant or native of ancient Rome,” from Latin Romanus “of Rome, Roman,”from Roma “Rome” (see Rome). The adjective is c. 1300, from Old French Romain. The Old English adjective was romanisc, which yielded Middle English Romanisshe. (pertaining to the ‘Holy Roman Empire”.)
SPACE
Etymology, origin and meaning of space
Online Etymology Dictionary
Apr 12, 2023 — 1300, “extent or area; room” (to do something), a shortening of Old French espace “period of time, distance, interval”(12c.), from Latin …
TELESCOPE
Telescope – Definition, Meaning & Synonyms – Vocabulary.com
Telescope is from the Greek roots tele.“far,” and skopos, “seeing;”so it literally describes what the instrument does. As a verb, telescope means “to become smaller through one part sliding into another,” the way a portable collapsing telescope does.
 The Large UV/Optical/Infrared Telescope would have a mirror between 8 and 16 meters wide and will collect light in all wavelengths. This is a massive space telescope that is too big for any current rockets, though could be carried up on the SLS, New Glenn, or SpaceX Starship.While similar to Hubble, LUVOIR will have 100 to 1,000 times the sensitivity, which it hopes to use to find the next “pale blue dot” and survey the birth and evolution of the cosmos. To achieve this range of science goals, LUVOIR will be well equipped with a range of instruments including a coronagraph, a high-definition imager, spectrograph, and spectropolarimeter.The mirror itself will depend on the version selected. LUVOIR-A would have a 15-meter primary mirror, and LUVOIR-B an 8-meter primary mirror. New, advanced mirror coatings will allow observations at wavelengths shorter than can be observed with Hubble, which opens up observations of highly ionized oxygen – -an important probe of hot gas across the universe. The team is still working on developing actuators to keep the mirror segments aligned as well as a way to isolate any vibrations, so they don’t affect the instruments’ measurements.
The Large UV/Optical/Infrared Telescope would have a mirror between 8 and 16 meters wide and will collect light in all wavelengths. This is a massive space telescope that is too big for any current rockets, though could be carried up on the SLS, New Glenn, or SpaceX Starship.While similar to Hubble, LUVOIR will have 100 to 1,000 times the sensitivity, which it hopes to use to find the next “pale blue dot” and survey the birth and evolution of the cosmos. To achieve this range of science goals, LUVOIR will be well equipped with a range of instruments including a coronagraph, a high-definition imager, spectrograph, and spectropolarimeter.The mirror itself will depend on the version selected. LUVOIR-A would have a 15-meter primary mirror, and LUVOIR-B an 8-meter primary mirror. New, advanced mirror coatings will allow observations at wavelengths shorter than can be observed with Hubble, which opens up observations of highly ionized oxygen – -an important probe of hot gas across the universe. The team is still working on developing actuators to keep the mirror segments aligned as well as a way to isolate any vibrations, so they don’t affect the instruments’ measurements.spacer
Lugh – Wikipedia
Lugh or Lug (Old Irish: [l̪ˠuɣˠ]; Modern Irish: Lú [l̪ˠuː]) is a figure in Irish mythology. A member of the Tuatha Dé Danann, a group of supernatural beings, Lugh is portrayed as a warrior, a king, a master craftsman and a savior. He is associated with skill and mastery in multiple disciplines, including the arts.
Lugh
The Irish god of nobility, Lugh of the Long Arm was a master of crafts and a cunning warrior. It has been suggested that the name stems from the Proto-Indo-European root lewgh-, meaning “to bind by oath.”This meaning would referencing Lugh’s role in regards to oaths and contracts.It has also been suggested that the name is connected to the word “light”. Lugh was a master of many talents. As the god of oaths, he held domain over rulers and nobility. He also served as the god of justice in its many forms; his judgement was often swift and without mercy. In what may seem like a contradiction, Lugh was also a trickster who was willing to lie, cheat, and steal to overcome his opponents.
As son of both the Tuatha Dé Danann and Fomorians, Lugh had a unique heritage. Such a background assisted him in inventing a number of notable Irish games, including horse-racing, sports, and fidchell, the Irish precursor to chess.
They Swore an Oath – Octagon
LU in the Collins Dictionary
LU in British English – physics
Lu in British English
lu in British English
THE INTERNET DOMAIN NAME FOR Luxembourg
Temple of BAAL – LUXEMBURG – ARCH of TRIUMPH or should we say VICTORY?
lu (Old French) Alternative forms lou, leu
Origin & history Reduced form of Latin lupus.
Noun lu (masc.) wolf
Lu/Lou is the root of the name Loup-garou, the French word for werewolf. Names containing the element wolf or wulf, like the German name Wolfgang, or the Old English name Wulfric.
MARS MISSION 2020
Israeli News Live / 398K subscribers / 8,462 views Jul 31, 2023
Video footage of an alleged Werewolf surfaces on Twitter, what we can add to this
makes it even more interesting. You decide!
lu (Tocharian A)
Origin & history
Probably from Proto-Indo-European *luhxeh₂, through a Proto-Tocharian *luwā-. Compare Tocharian B luwo. May be distantly related to Old Church Slavonic lovъ (“chase”), Serbo-Croatian lõv (“chase; game animal”); compare also Ancient Greek λέων.
Noun – lu animal
VOIR
Voir etymology in French
| video | English (eng) | (dated) VHS.. A short film clip, with or without audio (as in a music video, or one of the plethora of user-generated short movies on sites such as YouTube).. Motion picture stored on VHS or some other format.. Television, television show, movie. (Britain) To record a television program. (Britain) To record using a video camera, to videotape. |
spacer


Thirty Meter Telescope
 This massive ground-based telescope has faced numerous delays due to native Hawaiians protesting it being built on Mauna Kea, which they consider sacred land. This telescope would have 20x the power of Hubble.
This massive ground-based telescope has faced numerous delays due to native Hawaiians protesting it being built on Mauna Kea, which they consider sacred land. This telescope would have 20x the power of Hubble.
The Mystery of the Number Thirty | Living Word Discovery
The Living Word in 3D
Apr 24, 2017 — The picture meaning of the Hebrew Word Thirty agrees with the number meaning of 30. It is all about blood atonement and redemption. (SACRIFICE)
Biblical Meaning Of 30
Spiritual Learners
Apr 25, 2023 — The number 30 is a symbol of dedication, maturity, and preparation. Also the beginning of ministry or service.
Number 30 Symbolism, 30 Meaning and Numerology
RidingTheBeast.com
Dec 19, 1998 — Represent the perfect balance in the cosmic organization. · To Cabalistic, this number is associated with the letter “lamed”, in form of sickle ” “to express the maturity of the crop”. It corresponds also to the 12th Arcane of the Tarot, the Hanging,which is interpreted generally as the Expiation, the Sacrifice, the Martyrdom.
METER
What Is a Meter? Definition and Calculations
ThoughtCo
Feb 2, 2022 — The meter (m) is the SI unit of length or distance. · By definition, it is the distance light travels in a vacuum in 1/299792458 seconds. ·
TELESCOPE
Telescope – Definition, Meaning & Synonyms – Vocabulary.com
Telescope isfrom the Greek roots tele.“far,” and skopos, “seeing;” so it literally describes what the instrument does. As a verb, telescope means “to become smaller through one part sliding into another,” the way a portable collapsing telescope does.
Extremely Large Telescope
 Currently being built in the Atacama desert of Chile, this 39-meter wide mirrorwill focus on the infrared spectrum and should answer some of the biggest questions about universal expansion.
Currently being built in the Atacama desert of Chile, this 39-meter wide mirrorwill focus on the infrared spectrum and should answer some of the biggest questions about universal expansion.
The Extremely Large Telescope is an astronomical observatory currently under construction. When completed, it will be the world’s largest optical/near-infrared extremely large telescope. Part of the European Southern Observatory agency, it is located on top of Cerro Armazones in the Atacama Desert of northern Chile.
Etymology, origin and meaning of extremely by etymonline
1530s, from extreme + -ly (2). Originally “with great severity,” later more loosely, “in extreme degree” (1570s).Oct 26, 2012
extremely – definition and meaning
Wordnik
extremely: In the utmost degree; to the utmost; more commonly, to a very great degree; exceedingly: as, extremely hot or cold; extremely painful.
LARGE
large | Etymology, origin and meaning of large by etymonline
1200, of areas, “great in expanse,”of persons, “bountiful, inclined to give or spend freely,”from Old French large “broad, wide; generous, bounteous” (12c.), from Latin largus “abundant, copious, plentiful; bountiful, liberal in giving, generous” (source also of Spanish largo “long,” Italian largo “wide”), a word of …Aug 19, 2020
TELESCOPE
Telescope – Definition, Meaning & Synonyms – Vocabulary.com
Telescope isfrom the Greek roots tele.“far,” and skopos, “seeing;” so it literally describes what the instrument does. As a verb, telescope means “to become smaller through one part sliding into another,” the way a portable collapsing telescope does.
 Large Magellan Telescope /Giant Magellan TeleShootsscope
Large Magellan Telescope /Giant Magellan TeleShootsscopeConstructed out of 7 8-meter wide mirrors– the largest in the entire world – this telescope is the simplest of the telescopes, which should allow for optimal optics. The Giant Magellan Telescope is the most powerful telescope on Earth. It is designed to discover the unknown.
Shoots Lazers!!
giant (n.)
c. 1300, “fabulous man-like creature of enormous size,” from Old French geant, earlier jaiant “giant, ogre” (12c.), from Vulgar Latin *gagantem (nominative gagas),from Latin gigas “a giant,” from Greek Gigas (usually in plural, Gigantes), one of a race of divine but savage and monstrous beings (personifying destructive natural forces), sons of Gaia and Uranus, eventually destroyed by the gods. The word is of unknown origin, probably from a pre-Greek language. Derivation from gegenes “earth-born”is considered untenable.
In þat tyme wer here non hauntes Of no men bot of geauntes. [Wace’s Chronicle, c. 1330]
It replaced Old English ent, eoten, also gigant (from Latin). The Greek word was used in Septuagint to refer to men of great size and strength, hence the expanded use in modern languages; in English of very tall and unusually large persons from 1550s; of persons who have any quality in extraordinary degree from 1530s. As a class of stars, from 1912. As an adjective from early 15c. Giant-killer is from 1726.
Magellan
Name Magellan at Onomast. Meaning and origin of the name
Portuguese name Magalhães, comes from the ancient Greek word μεγᾰλο [mehalo] denotation – “great; lage, big; sizeable”. Ferdinand Magellan (c. 1480 – 27 April 1521) was a Portuguese explorer.
Magellan – [ muh–jel–uhn – noun
-
-
Ferdinand, c1480–1521, Portuguese navigator: discoverer of the Strait of Magellan 1520 and the Philippines 1521.
-
Strait of Magellan, Also Straits of Magellan . a strait near the southern tip of South Americabetween the mainland of Chile and Tierra del Fuego and other islands, connecting the Atlantic Ocean and the Pacific Ocean. 360 miles (580 kilometers) long
-
Tele/Shoots/scope
Tele
tele-
before vowels tel-, word-forming element meaning “far, far off, operating over distance”(also, since c. 1940, “television”), from Greek tele “far off, afar, at or to a distance,” related to teleos (genitive telos) “end, goal, completion, result,” from PIE root *kwel- (2) “far” in space or time.
Shoot Definition & Meaning
Dictionary.com|
verb (used with object),shot, shoot·ing. to hit, wound, damage, kill, or destroy with a missile discharged from a weapon.|
shoots
scope
-
1.the extent of the area or subject matter that something deals with or to which it is relevant.“we widened the scope of our investigation”
-
2.the opportunity or possibility to do or deal with something.“the scope for major change is always limited by political realities”
-
1.assess or investigate(something).“they’d scoped out their market”
-
2.INFORMAL•NORTH AMERICANlook at carefully; scan.“they watched him scoping the room, looking for Michael”
 FAST /The Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical radio Telescope, nicknamed Tianyan
FAST /The Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical radio Telescope, nicknamed TianyanThis Chinese radio telescope took the prize from Arecibo in Puerto Rico as the largest telescope in the world, and even though they’re still calibrating it, it has already discovered dozens of pulsars. Tianyan, is a radio telescope located in the Dawodang depression, a natural basin in Pingtang County, Guizhou, southwest China. FAST has a 500 m diameter dish constructed in a natural depression in the landscape
SPACER
Numerology 5 Meaning: Flexibility and Resilience
TheCoolist
Jan 11, 2023 — Numerology 5’s significance predominantly represents change, adventure, transformation, and luck.
5 Elements of Nature: wind, water, fire, light ether. In Occultism, 5 plays a prominent role in necromancy. Objects or people arranged in fives are believed to trap demons so they can be compelled to do humans’ bidding. five is such an indispensable number that its symbolic meanings are inexhaustible. Across cultures, 5 is believed to lead us to physical and spiritual awareness. It holds significance across religions, mythologies, and in a wide range of subjects, including math, science, astronomy, alchemy, and others. Source
Spiritual Meaning of Hundred
Bible Meanings
That the number a hundred signifies what is full, is evident from other passages in the Word, as in Isaiah:– There shall be no more
100 in Numerology: Angel Number Meaning and Symbolism
Apr 11, 2022 — It symbolizes enlightenment and self-realization. When you reach this number vibration, you have reached the pinnacle of your spiritual journey.
hundred (adj., n.)
“1 more than ninety-nine, ten times ten; the number which is one more than ninety-nine; a symbol representing this number;” Old English hundred “the number of 100, a counting of 100,” from Proto-Germanic *hunda-ratha- (source also of Old Frisian hundred, Old Saxon hunderod, Old Norse hundrað, German hundert); first element is Proto-Germanic *hundam “hundred” (cognate with Gothic hund, Old High German hunt), from PIE *km-tom “hundred,” reduced from *dkm-tom- (source also of Sanskrit satam, Avestan satem, Greek hekaton, Latin centum, Lithuanian šimtas, Old Church Slavonic suto, Old Irish cet, Breton kant “hundred”), suffixed form of root *dekm- “ten.”
The second element is Proto-Germanic *rath “reckoning, number”(as in Gothic raþjo “a reckoning, account, number,” garaþjan “to count;” from PIE root *re- “to reason, count”). The common word for the number in Old English was simple hund, and Old English also used hund-teontig.
In Old Norse hundrath meant 120, that is the long hundred of six score,and at a later date, when both the six-score hundred and the five-score hundred were in use, the old or long hundred was styled hundrath tolf-roett… meaning “duodecimal hundred,” and the new or short hundred was called hundrath ti-rætt, meaning “decimal hundred.” “The Long Hundred and its use in England” was discussed by Mr W.H. Stevenson, in 1889, in the Archæological Review (iv. 313-27), where he stated that amongst the Teutons, who longest preserved their native customs unimpaired by the influence of Latin Christianity, the hundred was generally the six-score hundred. The short hundred was introduced among the Northmen in the train of Christianity. [Transactions of the Lancashire and Cheshire Antiquarian Society, 1907] sixscore= Six times twenty; one hundred and twenty.
METER
What Is a Meter? Definition and Calculations
ThoughtCo
Feb 2, 2022 — The meter (m) is the SI unit of length or distance. · By definition, it is the distance light travels in a vacuum in 1/299792458 seconds. ·
Aperture
Etymology, origin and meaning of aperture by etymonline
(Chaulisc), “an opening, hole, orifice,” from Latin apertura “an opening,”from apertus, past participle of aperire “to open, uncover,” from PIE compound *ap-wer-yo- from *ap- “off, away”(see apo-) + root *wer- (4) “to cover.” In optics, “the diameter of the exposed part of a telescope, microscope, etc.,” from 1660s.Sep 23, 2022
a re-Latinized spelling, attested beginning mid-15c., of Middle English spere (c. 1300) “cosmos; space, conceived as a hollow globe about the world,”from Anglo-French espiere, Old French espere (13c., Modern French sphère), from Latin sphaera “globe, ball, celestial sphere” (Medieval Latin spera), from Greek sphaira “globe, ball, playing ball, terrestrial globe,”a word of unknown origin.
spherical (adj.)
1520s, “bounded by or having the form of the surface of a sphere,”from sphere + -ical. The sense of “pertaining to or related to a sphere or spheres” is from c. 1600. Related: Spherically.
A spherical number (1640s) is one whose powers always terminate in the same digit as the number itself: 5, 6, and 10.
radio
radio- | Meaning of prefix radio
Jun 2, 2013 — 1400, “of or like a ray or radius,” from Medieval Latin radialis, from Latin radius “shaft, rod; spoke of a wheel; beam of light”(see radius).
“wireless transmission of voice signals with radio waves,”1907, abstracted or shortened from earlier combinations such as radio-receiver (1903), radiophone “instrument for the production of sound by radiant energy” (1881), radio-telegraphy “means of sending telegraph messages by radio rather than by wire” (1898), from radio- as a combining form of Latin radius “beam”(see radius). Use for “radio receiver” is attested by 1913; sense of “sound broadcasting as a medium”also is from 1913.
TELESCOPE
Telescope – Definition, Meaning & Synonyms – Vocabulary.com
Telescope isfrom the Greek roots tele.“far,” and skopos, “seeing;” so it literally describes what the instrument does. As a verb, telescope means “to become smaller through one part sliding into another,” the way a portable collapsing telescope does.
Tianyan
Home – The Meaning Of The Name
Tian-Yan is a first name used for both boys and girls. Growth number: 3. Find all about this name: meaning, origin and numerology interpretation.
Tian | Chinese Religion & Philosophy – Britannica
tian,(Chinese: “heaven” or “sky”)Wade-Giles romanization t’ien, in indigenous Chinese religion, the supreme power reigning over lesser gods and human beings.The term tian may refer to a deity, to impersonal nature, or to both.
Yan – Baby Name Meaning, Origin and Popularity – The Bump
Yan is a feminine name of Chinese origin that means “beautiful.” Yan has been used as a surname and a place name throughout China and is steeped in antiquity.
 Large Synoptic Survey Telescope/ The Vera C. Rubin Observatory
Large Synoptic Survey Telescope/ The Vera C. Rubin ObservatoryWhile not impressively huge, the LSST is exciting because of how it will be used – to scan the entire sky every 3 days. Over 10 years, the amount of data this telescope will produce will equal 50 petabytes and could help find new planetary objects in our own solar system.
The DOE-funded effort to build the Rubin Observatory LSST Camera (LSSTCam) is managed by the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory (SLAC).
The Vera C. Rubin Observatory, currently under construction on Cerro Pachón in Chile, will conduct an unprecedented, decade-long survey of the optical sky called the Large Survey of Space and Time (LSST). The Rubin Observatory has a wide-field reflecting telescope with an 8.4-meter primary mirror that will photograph the entire available sky every few nights. The telescope uses a novel 3-mirror design, a variant of TMA (Three-Mirror Anastigmat), which allows a compact telescope to deliver sharp images over a very wide 3.5º diameter field of view.
Location: The telescope is located on the El Peñón peak of Cerro Pachón, a 2,682-meter-high mountain in the Coquimbo Region, in northern Chile, alongside the existing Gemini South and Southern Astrophysical Research Telescopes (location: 30º14’40.68”S, 70º44’57.90”W). The LSST Base Facility is located about 100 km away by road, in the town of La Serena. 1)
Vera
Vera
fem. proper name, from Latin, literally “true” (see very).
Vera Definition & Meaning
YourDictionary
Borrowed in the nineteenth century from the Russian virtue name Вера (Véra, “faith” ). By folk etymology it has also been explained as Latin vera (“true” ).
C.
C. Letter C Symbolism and meaning
Gimel is the third letter in the Hebrew alphabet, meaning camel, corresponding to letter C, or G. Both are good with words because their numerical root is 3. Gimel is associated with riches because camels were often laden with many rich possessions.
In esoteric teachings, Gimel is the Ternary Law that arises to resolve the opposite of the Monad (A-1) and Duad (B-2). It is the symbol of the Holy Trinity of Will, Wisdom, and Love. It connects and harmonizes Aleph and Beth together. C is the first letter of Christ, representing the spiritual consciousness within its nature.
Spiritually, C also symbolizes the Word of God. Every cell in our body reacts to the things that we say. In occult science, words literally cast spells, which is the reason why we have the word “Spelling”.
When the Romans borrowed the glyph of Gimel (G), they created a second symbol C for “K” sound, to distinguish the pronunciation.
C is pronounced “sea”, whose shape is the half-moon, representing our subconsciousness and the Mother (moon). C also sounds like “see” and is facing the right. Therefore, C has psychic ability to see the future.
In Egypt, C stands for Circle of gods, which are the Company of gods standing on the Day of Judgement, according to Resurrect Isis. When we double the C, we have letter O, which is symbolic of the Council Circle. That’s why when the legislators of the U.S sit in a formal meeting, they usually sit in a Circle, or the round table.

The symbol of C is similar to that of our outer ears. C represents our spiritual faculty of hearing, which is the ability to hear the sounds of silence, the voice of God, and the vibration of higher realms.
The Egyptians believe that letter C is an emblem of Noah’s Ark, which is related to the Arc of Osiris. This is why the shape of the rainbow also has the curve of letter C, representing the Sign and Power of God.
Rubin
Extreme Coronagraph for Living Planetary Systems
The LUVOIR Extreme Coronagraph for Living Planetary Systems (ECLIPS) I: Searching and Characterizing Exoplanetary Gems Detection and characterization of Earth-like planets around nearby stars using the direct imaging technique is a key scientific objective of future NASA astrophysics flagship missions. As a result, dedicated exoplanet instruments are being studied for the Large UV/Optical/Infrared Surveyor (LUVOIR) and the Habitable Exoplanet Imager (HabEx) mission concepts. In this paper we discuss the Extreme Coronagraph for Living Planetary Systems (ECLIPS) instrument of LUVOIR. ECLIPS will be capable of providing starlight suppression levels of ten orders of magnitude over a broad range of wavelengths in order to detect and characterize the light reflected from potentially Earth-like planets. It will also allow future astronomers to study in great detail the diversity of exoplanets.
First, we review the main science drivers and emphasize those that are the most stressing on the instrument design. We then present the overall parameters of the instrument (general architecture and back-end camera). We delve into the details of the static coronagraph masks, which have a significant impact on the scientific productivity of the mission. We discuss the choices the LUVOIR team made in order to maximize the discovery yield of exoEarth candidates. We then present our work on the technological feasibility of such an instrument, focusing in particular on the image stability necessary to achieve ten orders of magnitude of starlight extinction over hours of exposure. We present our error budget and show that using a combination of instrument level (low and high order wavefront sensors) and observatory level telemetry can yield an overall architecture that meets these requirements. Finally, we discuss future technology development efforts that will mature these technologies.
217K subscribers
spacer
 |
 |
| HABEX – Habitable Exoplanet Observatory | LYNX = The Lynx X-ray Observatory |
 |
 |
| ORIGINS – Origins Space Telescope | LUVOIR – Large UltraViolet Optical and Infrared Surveyor |
“capable of being inhabited or dwelt in; suited to serve as an abode for human beings,” late 14c., from Old French habitable “suitable for human dwelling” (14c.), from Latin habitabilis “that is fit to live in,” from habitare “to live, inhabit, dwell,” frequentative of habere “to have, to hold, possess” (from PIE root *ghabh- “to give or receive”).
WHAT IS AN EXOPLANET?
SETI Institute
Nov 10, 2020 — The prefix exo is short for extrasolar, meaning beyond the Sun, so exoplanets are just planets that orbit stars other than our Sun.
moderate-sized wildcat with a short tail, penciled ears, more or less spotted fur, and 28 teeth, inhabiting Eurasia, Africa, and North America; mid-14c., from Latin lynx (source of Spanish, Portuguese, Italian lince), from Greek lyngx, an old name of the lynx found also in Armenian, Germanic, and Balto-Slavic, though often transformed or altered. Often linked to PIE root *leuk- “light, brightness,” in reference to its gleaming eyes or its ability to see in the dark, but there are phonetic problems with that and Beekes suggests a loan from a non-IE substrate language.
If that men hadden eyghen of a beeste that highte lynx, so that the lokynge of folk myghte percen thurw the thynges that withstonden it. [Chaucer’s “Boethius,” c. 1380]
Cognates probably are Lithuanian lūšis “lynx,” Old High German luhs, German luchs, Old English lox, Dutch los, Swedish lo, Armenian lusanunk’. The dim northern constellation was added in 1687 by Johannes Hevelius. Lyncean “pertaining to a lynx” (from Greek lynkeios) is attested from 1630s.
Lynx (mythology) – Wikipedia
It is also believed to have supernatural eyesight, capable of seeing even through solid objects. As a result, it often symbolizes the unravelling of hidden truths, and the psychic power of clairvoyance.
Lynx
Blogger
Sep 9, 2012 — The power animal Lynx represents secrets. Lynx is the keeper of that which is hidden; knowing ancient secrets of time.
X-ray – nounˈeks-ˌrā
1: any of the electromagnetic radiations that have an extremely short wavelength of less than 100 angstroms and have the properties of penetrating various thicknesses of all solids, of producing secondary radiations by impinging on material bodies, and of acting on photographic films and plates as light does
2 : a photograph obtained by use of X-rays
Observatory
Observatory – Definition, Meaning & Synonyms | Vocabulary.com
Observatory comes from the verb observe, or “watch,” which in turn is rooted in the Latin observare, “watch over or guard.”
Origin – Definition, Meaning & Synonyms – Vocabulary.com
The origin of the word origin is the Latin word originem, meaning “rise, beginning, or source.” Definitions of origin. the place where something begins, where it springs into being.
1831, “pertaining to origins,” coined by Carlyle as if from Greek genetikos from genesis “origin” (see genesis). Darwin used it biologically as “resulting from common origin” (1859); modern sense of “pertaining to genetics or genes” is from 1908 (see gene). Related: Genetically. Genetical is attested from 1650s as “pertaining to origins.”
spacer
We have already seen that GOD created the Earth, the Sun, Moon and Stars and place them under the firmament. ALL of them are near to earth. There is nothing above the firmament but WATER!! A dark empty void except for the Throne of GOD, the Father and Son and all the Angels.
We can see the stars with our own eyes. Planets are not what “Science” claims. They are merely stars that do not hold their place, they move about within the Firmament.
When God had the following conversation with Abraham, He took Abraham outdoors and told him to look up and see ALL the STARS.
spaer
3 And Abram said, Behold, to me thou hast given no seed: and, lo, one born in my house is mine heir.
4 And, behold, the word of the Lord came unto him, saying, This shall not be thine heir; but he that shall come forth out of thine own bowels shall be thine heir.
5 And he brought him forth abroad, and said, Look now toward heaven, and tell the stars, if thou be able to number them: and he said unto him, So shall thy seed be.
spacer
Rollable ‘membrane mirrors’ could pave way for bigger, more powerful space telescopes
published
‘It could make lightweight mirrors that are 15 or 20 meters in diameter a reality.’

A newly developed way to make telescope mirrors could enable much larger, and thus more sensitive, telescopes to be placed in orbit. (Image credit: Sebastian Rabien, Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics)
A scientist says it may be possible to create low-cost foldable telescope mirrors that are more than twice the size of those onboard the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), whose giant iconic golden honeycomb mirror is the largest ever sent to space.
JWST‘s network of 18 gold-coated segments make up a primary mirror that’s 21 feet, 4 inches (6.5 meters) in diameter. Now, a scientist has come up with a new method to produce extremely large telescope mirrors that he thinks will be thinner, lighter and more affordable than many of the optics currently in orbit.
This new way “could help solve weight and packaging issues for telescope mirrors, enabling much larger, and thus more sensitive, telescopes to be placed in orbit,” Sebastian Rabien, a scientist at the Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics in Germany and the sole author of a new study detailing the tech, said in a statement.
Related: Giant next-generation space telescopes could be built off Earth

Using his new method, Rabien built a mirror 0.9 feet (30 centimeters) wide. He created what is called a membrane mirror by placing an evaporated material, the identity of which is not disclosed in the statement, into a vacuum chamber. Soon after, a lightweight polymer membrane, likely as thin as household plastic wrap, began to form.
Next, to mold this membrane into a parabola — a necessity for space telescopes, as the shape allows better focus by directing incoming light into one spot — Rabien added a “rotating container filled with a small amount of liquid” to the inside of the vacuum chamber. This allowed the polymer to grow and form the base of the mirror. Coating the mirror with a reflecting surface like aluminum would make it telescope-worthy, according to the statement.
Rabien proposes using his new method to create massive telescope mirrors, which are usually complicated and expensive to put together. (For example, it took the JWST team eight years to build the telescope’s mirrors.) The method has the potential to create mirrors that scale beyond the sizes of those onboard current space telescopes, the statement notes.
“Although this work only demonstrated the feasibility of the methods, it lays the groundwork for larger packable mirror systems that are less expensive,” Rabien said in the same statement. “It could make lightweight mirrors that are 15 or 20 meters [49 to 66 feet] in diameter a reality, enabling space-based telescopes that are orders of magnitude more sensitive than ones currently deployed or being planned.”
These large mirrors could be “rolled up” to fit compactly onto rockets to ride safely to orbit, Rabien believes. Once aloft, Rabien envisions flawless deployment of the mirrors, thanks to another method he developed that would use heat to ease out any kinks that would form after the mirrors unfold. Such gigantic sizes would, in turn, make telescopes bigger and more sensitive, allowing astronomers to collect higher quality observations.
Rabien details his research in a study published this month in the journal Applied Optics.
A similar was undertaken in 2010 by the U.S. military’s advanced research wing, the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), which funded a project to explore replacing traditional telescope mirrors with a polymer membrane. The goal was to create a lightweight foldable space telescope that could capture real-time videos and images of Earth in high resolution.
DARPA’s funding for the project — known as the Membrane Optical Imager for Real-Time Exploitation, or MOIRE — was mostly intended for the country’s warfighters, but the project’s scope extended into planetary exploration too. MOIRE’s prime contractor, Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., said at the time that the “game-changing approach” would “dwarf” any telescope projects under development at the time, including JWST.
However, there has been little news after the project prototype was tested in late 2013, and it has apparently not been used as a part of a space mission to date.
Follow Sharmila Kuthunur on Twitter @Sharmilakg. Follow us on Twitter @Spacedotcom and on Facebook.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.
spacer
World’s largest liquid mirror telescope ready to observe
published
Astronomers must brave a 10-hour drive into the Himalayas to get there.

The ILMT mirror during testing at Liège in Belgium. (Image credit: Prof. Jean Surdej, Univ. of Liege, Liege, Belgium)
The world’s largest liquid mirror telescope is ready to gaze at the stars.
Located at the Devasthal Observatory in India’s Himalayas, at an elevation of 8,038 feet (2,450 meters), the four-meter International Liquid Mirror Telescope (ILMT) is the first liquid telescope to be built specifically for astronomy.
Most telescopes use glass mirrors, but as the ILMT’s name suggests, its mirror is made from a thin layer of liquid mercury that floats on 10 microns of compressed air and rotates every eight seconds. “By way of comparison, a human hair is approximately 70 microns thick,” Paul Hickson, an astronomer at the University of British Columbia who helped develop the telescope, said in a statement. “The air bearings are so sensitive that even smoke particles can damage them.”
The tradeoff is that the ILTM is fixed in a single position, so it only observes one strip of the night sky as the Earth rotates below it. But since the telescope will be hyper-focused on just one area, it’s well-suited for spotting transient objects like supernovas and asteroids.
“The collected data will be ideally suited to perform a deep photometric and astrometric variability survey over a period of typically five years,” Jean Surdej, project director and an astrophysicist at the University of Liège, Belgium, and the University of Poznan, Poland, said in the statement.
Expected to begin science observations later this year, the ILTM will operate from October through June annually, closing during India’s rainy season. The project is an international collaboration between institutions in India, Belgium, Poland, Uzbekistan and Canada.
Follow Stefanie Waldek on Twitter @StefanieWaldek. Follow us on Twitter @Spacedotcom and on Facebook.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.
spacer

s[acer
Gallery: The Giant Magellan Telescope Envisioned in Chile
published
 |
 |
|
An artist’s illustration of the completed Giant Magellan Telescope atop Las Campanas Peak in Chile’s Atacama Desert. It will be one of the largest on Earth when it is completed in 2018. |
An artist’s illustration of the completed Giant Magellan Telescope atop Las Campanas Peak in Chile’s Atacama Desert. The 82-foot (24.5-meter) telescope will be one of the largest on Earth when it is completed in 2018. |
 |
 |
|
An artist’s illustration of the completed Giant Magellan Telescope atop Las Campanas Peak in Chile’s Atacama Desert. The 82-foot (24.5-meter) telescope will consist of six smaller, circular mirrors and feature an advanced adaptive optics system. It will be one of the largest on Earth when it is completed in 2018. |
An artist’s illustration of the completed Giant Magellan Telescope atop Las Campanas Peak in Chile’s Atacama Desert. The 80-foot (24.5-meter) telescope will consist of seven primary mirrors and feature an advanced adaptive optics system. It will be one of the largest on Earth when it’s up and running in 2020. |

An artist’s illustration of the completed Giant Magellan Telescope atop Las Campanas Peak in Chile’s Atacama Desert. The 82-foot (24.5-meter) telescope will be one of the largest on Earth when it is completed in 2018.
Giant New Telescope Gets $50 Million In Funding

The Giant Magellan Telescope: Artist’s View

An artist’s illustration of the completed Giant Magellan Telescope atop Las Campanas Peak in Chile’s Atacama Desert. The 82-foot (24.5-meter) telescope will consist of six smaller, circular mirrors and feature an advanced adaptive optics system. It will be one of the largest on Earth when it is completed in 2018.
Giant Magellan Telescope conception

Giant Magellan Telescope – mirror polishing

Giant Magellan Telescope – mirrors

Giant Magellan Telescope Site in Chile

Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.
spacer
The Vera C. Rubin Observatory is perhaps the next most exciting observatory to the James Webb Space Telescope. So why is it that hardly anyone has heard of it? Displate 20% off link: https://displate.com/promo/astrum?art…
spacer
After a three-year hiatus, scientists in the U.S. have just turned on detectors capable of measuring gravitational waves – tiny ripples in space itself that travel through the universe.
Unlike light waves, gravitational waves are nearly unimpeded by the galaxies, stars, gas and dust that fill the universe. This means that by measuring gravitational waves, astrophysicists like me can peek directly into the heart of some of these most spectacular phenomena in the universe.
Since 2020, the Laser Interferometric Gravitational-Wave Observatory – commonly known as LIGO – has been sitting dormant while it underwent some exciting upgrades. These improvements will significantly boost the sensitivity of LIGO and should allow the facility to observe more-distant objects that produce smaller ripples in spacetime.
By detecting more events that create gravitational waves, there will be more opportunities for astronomers to also observe the light produced by those same events. Seeing an event through multiple channels of information, an approach called multi-messenger astronomy, provides astronomers rare and coveted opportunities to learn about physics far beyond the realm of any laboratory testing.
Ripples in spacetime
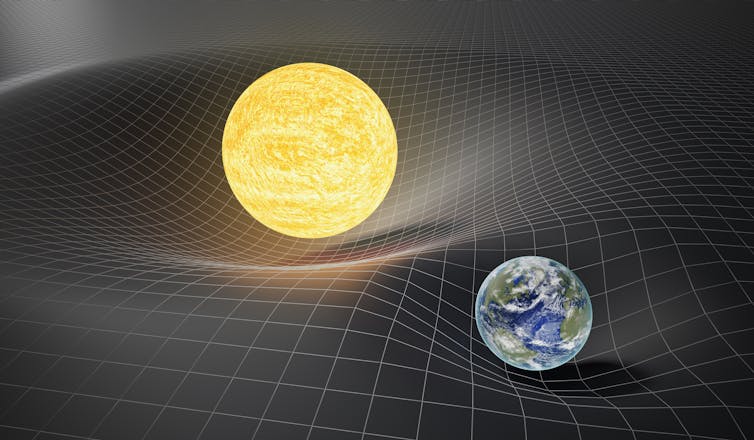
According to Einstein’s theory of general relativity, mass and energy warp the shape of space and time. The bending of spacetime determines how objects move in relation to one another – what people experience as gravity.
Gravitational waves are created when massive objects like black holes or neutron stars merge with one another, producing sudden, large changes in space. The process of space warping and flexing sends ripples across the universe like a wave across a still pond. These waves travel out in all directions from a disturbance, minutely bending space as they do so and ever so slightly changing the distance between objects in their way.
Even though the astronomical events that produce gravitational waves involve some of the most massive objects in the universe, the stretching and contracting of space is infinitesimally small. A strong gravitational wave passing through the Milky Way may only change the diameter of the entire galaxy by three feet (one meter).
The first gravitational wave observations
Though first predicted by Einstein in 1916, scientists of that era had little hope of measuring the tiny changes in distance postulated by the theory of gravitational waves.
Around the year 2000, scientists at Caltech, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and other universities around the world finished constructing what is essentially the most precise ruler ever built – the LIGO observatory.
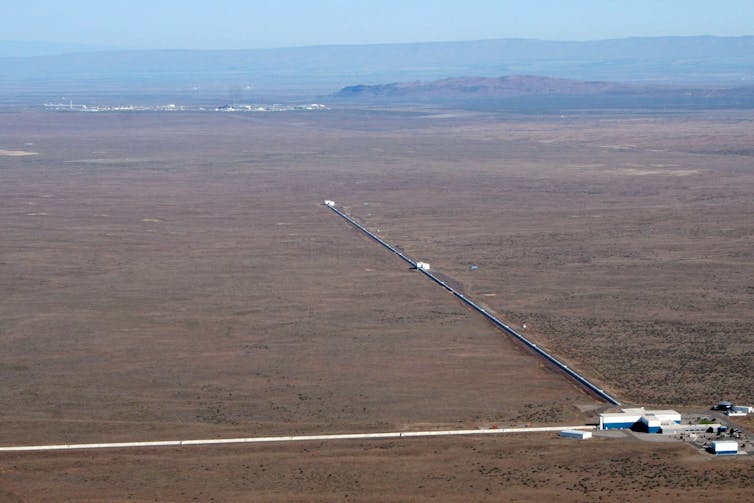

LIGO is comprised of two separate observatories, with one located in Hanford, Washington, and the other in Livingston, Louisiana. Each observatory is shaped like a giant L with two, 2.5-mile-long (four-kilometer-long) arms extending out from the center of the facility at 90 degrees to each other.
To measure gravitational waves, researchers shine a laser from the center of the facility to the base of the L. There, the laser is split so that a beam travels down each arm, reflects off a mirror and returns to the base. If a gravitational wave passes through the arms while the laser is shining, the two beams will return to the center at ever so slightly different times. By measuring this difference, physicists can discern that a gravitational wave passed through the facility.
LIGO began operating in the early 2000s, but it was not sensitive enough to detect gravitational waves. So, in 2010, the LIGO team temporarily shut down the facility to perform upgrades to boost sensitivity. The upgraded version of LIGO started collecting data in 2015 and almost immediately detected gravitational waves produced from the merger of two black holes.
Since 2015, LIGO has completed three observation runs. The first, run O1, lasted about four months; the second, O2, about nine months; and the third, O3, ran for 11 months before the COVID-19 pandemic forced the facilities to close. Starting with run O2, LIGO has been jointly observing with an Italian observatory called Virgo.
Between each run, scientists improved the physical components of the detectors and data analysis methods. By the end of run O3 in March 2020, researchers in the LIGO and Virgo collaboration had detected about 90 gravitational waves from the merging of black holes and neutron stars.
The observatories have still not yet achieved their maximum design sensitivity. So, in 2020, both observatories shut down for upgrades yet again.

Making some upgrades
Scientists have been working on many technological improvements.
One particularly promising upgrade involved adding a 1,000-foot (300-meter) optical cavity to improve a technique called squeezing. Squeezing allows scientists to reduce detector noise using the quantum properties of light. With this upgrade, the LIGO team should be able to detect much weaker gravitational waves than before.
My teammates and I are data scientists in the LIGO collaboration, and we have been working on a number of different upgrades to software used to process LIGO data and the algorithms that recognize signs of gravitational waves in that data. These algorithms function by searching for patterns that match theoretical models of millions of possible black hole and neutron star merger events. The improved algorithm should be able to more easily pick out the faint signs of gravitational waves from background noise in the data than the previous versions of the algorithms.
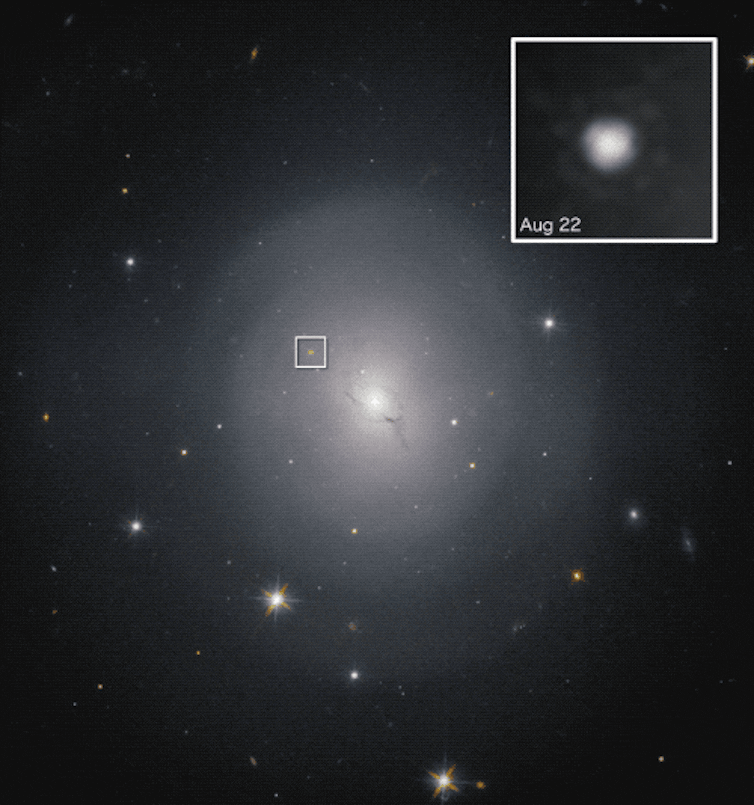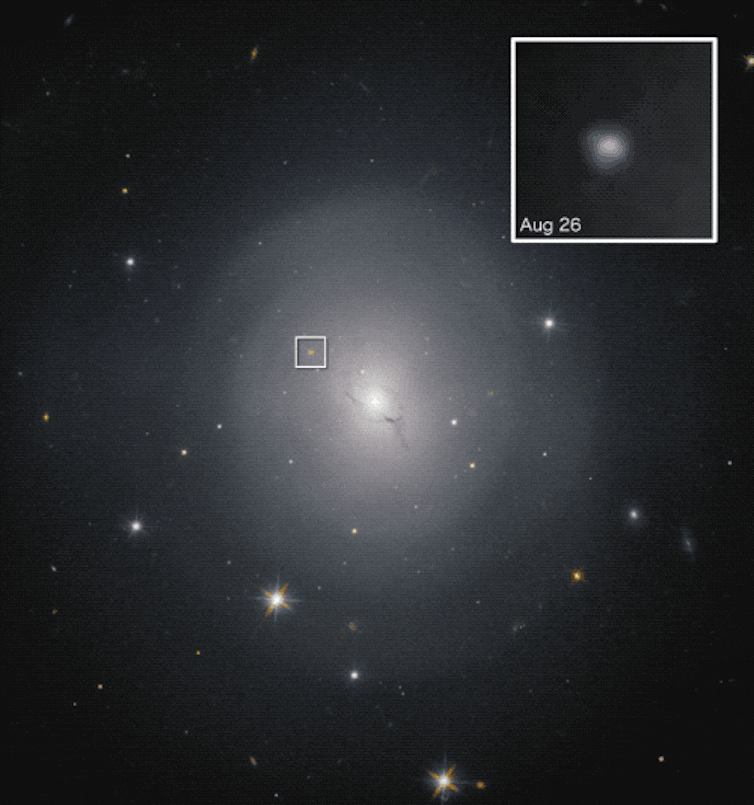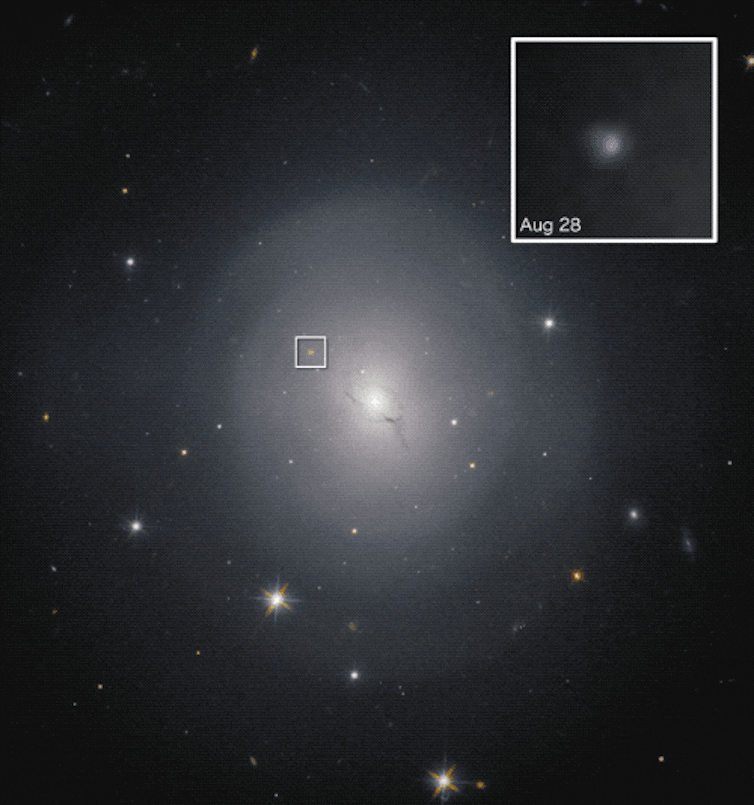
A hi-def era of astronomy
In early May 2023, LIGO began a short test run – called an engineering run – to make sure everything was working. On May 18, LIGO detected gravitational waves likely produced from a neutron star merging into a black hole.
LIGO’s 20-month observation run 04 will officially start on May 24, and it will later be joined by Virgo and a new Japanese observatory – the Kamioka Gravitational Wave Detector, or KAGRA.
While there are many scientific goals for this run, there is a particular focus on detecting and localizing gravitational waves in real time. If the team can identify a gravitational wave event, figure out where the waves came from and alert other astronomers to these discoveries quickly, it would enable astronomers to point other telescopes that collect visible light, radio waves or other types of data at the source of the gravitational wave. Collecting multiple channels of information on a single event – multi-messenger astrophysics – is like adding color and sound to a black-and-white silent film and can provide a much deeper understanding of astrophysical phenomena.
Astronomers have only observed a single event in both gravitational waves and visible light to date – the merger of two neutron stars seen in 2017. But from this single event, physicists were able to study the expansion of the universe and confirm the origin of some of the universe’s most energetic events known as gamma-ray bursts.
With run O4, astronomers will have access to the most sensitive gravitational wave observatories in history and hopefully will collect more data than ever before. My colleagues and I are hopeful that the coming months will result in one – or perhaps many – multi-messenger observations that will push the boundaries of modern astrophysics.
spacer
Ligo – wiktionary
ligo – Verb
- to take a bath
- to swim
- to give someone a bath
- to shower; to bestow liberally, to give or distribute in abundance
ligo – Noun
- a bath
ligo (Spanish, Portuguese, Latin): meaning, translation
WordSense Dictionary
Verb. ligo. I tie, bind. I bandage, wrap around. I unite. Derived words & phrases.
Ligo meaning in English
DictZone
ligo, necto verb. tie ▽ (to attach or fasten with string) verb [UK: taɪ] [US: ˈtaɪ]. adalligo [adalligare, adalligavi, adalligatus] (1st) TRANS
Ligo Meaning
- n.paligo’ (pa-) bathing paliguan (pa-an)
- n.bathroom, bathing place
- v.maligo (ma-) to take a bath or shower, to bathe. Naligo siya sa ilog. He went for a dip in the river.
Ligo Meaning, Pronunciation, Origin and Numerology
NamesLook
Ligo Meaning · Meaning: Investigator, Care Taker
Religion and Revelation After Auschwitz
By Balazs M. Mezei



LIGO detects merging black holes for third time | MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology

Gravitational waves — and light — seen in neutron star collision
BY WILLIAM HARWOOD
/ CBS NEWS


“The combined information of gravitational waves and light is bigger than the sum of its parts,” she said. “From the combined information we’re learning new things about physics, about the universe, about the elements we’re made of.”
An astronomical gold mine of sorts. Literally.
Theorists have long speculated that neutron star mergers could generate the enormous energies needed to synthesize elements heavier than iron. Supernova explosions also create heavy elements, but they alone cannot explain the observed abundances of gold, platinum, uranium and other heavy elements.
Analysis of light from the Aug. 17 kilonova event indicates the neutron star collision in a galaxy known as NGC 4883 did, in fact, seed the local environment with a flood of heavy elements.
The combined observations “revealed details that we’ve never seen before in any astronomical event, the direct fingerprints of the heaviest elements in the periodic table — gold, platinum, and other elements,” said Edo Berger, a Harvard University astronomer who led a team of observers.

“From the properties of the visible and infrared light, we conclude the total mass of heavy elements produced in this one single event is 16,000 times the mass of the Earth,” he said. “Of this material, we estimate that about 10 times the mass of the Earth is in gold and platinum alone. So imagine this as you gaze at your jewelry or invest in gold futures.”
The gravitational waves were detected at 8:41 a.m. on Aug. 17 by the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory, or LIGO, which in 2015 made the first detection of gravity waves generated by the merger of two black holes — a discovery that won the 2017 Nobel Prize in Physics.
This time around, the gravity waves were followed in seconds by detection of high-energy gamma rays by NASA’s Fermi Space Telescope. It was the first direct confirmation that gravitational radiation travels at the speed of light.
FERMI
Fermi Definition & Meaning | Dictionary.com
[ fur-mee; Italian fer-mee ] show ipa. nounPhysics. a unit of length, 10−15 m, used in measuring nuclear distances. femtometer.
Fermi – Definition, Meaning & Synonyms
Vocabulary.com
a metric unit of length equal to one quadrillionth of a meter.
fermi: meaning, definition
wordsense.eu
Origin & history. From French fermer. Verb. fermi. (transitive) to close, to shut. Fermu la fenestron! Mi estas malvarmega!
Meaning, origin and history of the surname Fermi
Behind the Name
Originally indicated a person from the town of Fermo in the Marche region of Italy, originally called Firmum in Latin meaning “strong, steady, firm“.
fermium | Etymology, origin and meaning of fermium
Online Etymology Dictionary
Jun 11, 2015 — Origin and meaning of fermium: radioactive element, discovered in the debris of a 1952 U.S. nuclear test in the Pacific, named 1955 for .
Within the next few hours, more than 70 observatories around the world, along with seven space-based instruments, were on the look out for an optical counterpart.
Astronomers with the Carnegie Institution for Science and the University of California at Santa Cruz were the first to pinpoint the collision using the 1-meter Swope Telescope at the Cerro Las Campanas observatory in Chile. They spotted a brilliant blue “star” in the galaxy NGC 4883 in the constellation Hydra.

Along with visible light, astronomers quickly detected infrared radiation, ultraviolet emissions, X-rays and radio waves as the object faded from blue to red, all expected signals from a cataclysmic event like the merger of two neutron stars.
“We finally now know what happens when an unstoppable force meets and immovable object,” said Andy Howell, a University of California-Santa Barbara astronomer. “And the answer is a kilonova.”
Tony Piro, leader of the Carnegie team, said in a statement “the ability to study the same event with both gravitational waves and light is a real revolution in astronomy. We can now study the universe with two completely different probes, which teach us things we could never know with only one or the other.”
LIGO has detected multiple black hole mergers, but black holes are, by definition, black, they do not generate light and cannot be directly seen. Astronomers predicted neutron star collisions would be visible if astronomers knew where to look.
The combination of LIGO’s gravity wave detection and Fermi’s detection of gamma rays narrowed the search and paved the way for the Swope telescope and others to find the cosmic needle in an equally cosmic haystack.
“We saw a bright blue source of light in a nearby galaxy, the first time the glowing debris from a neutron star merger had ever been observed,” Carnegie astronomer Josh Simon said in a statement. “It was definitely a thrilling moment.”

Simon and Carnegie astronomer Ben Shappee then used spectrographs mounted on the observatory’s huge 6.5-meter Magellan telescopes to analyze the light.
“As we followed the glow of the explosion over the next few weeks, it showed some key characteristics of the radioactive decay of these heavy elements,” said Maria Drout, a Carnegie researcher who helped guide the search. “This strongly suggests that these elements were synthesized following the merger, solving a 70-year-old mystery.”
One yet-to-be-answered question: what sort of body was left after the two neutron stars merged?
“There are some signs, some observations that have been made that suggest it should be a black hole,” said David Shoemaker, LIGO’s lead spokesman. “But in terms of its mass and all of the gravitational wave data, it could be either one of the heaviest neutron stars that’s ever been seen or one of the very lightest black holes that’s ever been seen.”
Eleonora Torja at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center believes the X-ray data shows a black hole is the most likely result.
“Very likely, the collision of two neutron stars resulted in a new black hole,” she said. “And this black hole ejected a high-speed jet of energy and matter. This jet was carrying the same amount of energy that our sun radiates over millions of years, and it was expanding at close to the speed of light.”
Neutron stars represent one of three possible outcomes when stars grow old, exhaust their nuclear fuel and either fade away or explode.
Stars like the sun remain stable, in a state of hydrostatic equilibrium, by balancing the outward pressure generated by nuclear fusion in the core with the inward pull of gravity. When a star runs out of nuclear fuel, fusion in the core stops, gravity takes over, the core collapses and the star’s outer layers are blown away into space.
For stars like the sun — and more than 90 percent of the stars in the Milky Way — core collapse is halted by a quantum effect known as electron degeneracy pressure, produced when electrons are squeezed as closely together as allowed in normal matter. The result is a white dwarf, a slowly cooling stellar remnant with up to 1.44 times the sun’s mass packed into a body the size of a small planet.
For larger stars, electron degeneracy is not enough to halt the core’s collapse when it runs out of fuel. Instead, gravity squeezes the core to the point where electrons merge with protons to form a neutron star, a bizarre city-size body just a few miles across with a mass of two to three times that of the sun.
“Neutron stars are the hardest things in the universe, harder than a cue ball, harder than diamond, and we really wanted to see what would happen if you smashed two of them together at near the speed of light,” said Howell.
“Neutron stars are like a giant atomic nucleus, only one 10 miles in diameter and composed entirely of neutrons. So this is like a cosmic scale atom smasher at energies far beyond what humans will ever be capable of building.”
For collapsing stars with even more massive cores, gravity overcomes even the neutron degeneracy pressure that otherwise would create a neutron star. The doomed sun becomes a black hole with many times the mass of the sun concentrated in what amounts to an invisible gravitational sinkhole.

Gravitational wave astronomy offers a powerful new way to study such high-energy events.
Einstein predicted the existence of gravitational waves in 1916 in his general theory of relativity. The equations indicated that massive bodies under acceleration, like two merging black holes, neutron stars or the collapsing cores of huge stars in the death throes of supernova explosions, would radiate gravitational energy in the form of waves distorting the fabric of spacetime.
The LIGO observatory features two stations, one in Washington and the other in Louisiana, that each feature a pair of 2.5-mile-long vacuum tubes arranged in an L shape in which precisely tuned laser beams flash back and forth between multiple mirrors. A gravitational wave stretches space in one direction and compress it in a perpendicular direction.
The effects on local space are infinitesimal, making detection a high-technology challenge and a feat Einstein could never have imagined. The LIGO equipment is sensitive enough to measure changes in the distance traveled by the laser beams to less than the width of a proton.
On Sept. 14, 2015, LIGO recorded gravitational radiation for the first time. Analyzing the data, scientists realized they had the tell-tale signature of two black holes merging. The discovery was announced the following February.