The HOT TOPIC of our day seems to be SMART. Smart everything and anything. Recently I saw a commercial on Television regarding Alexa and how to “SMARTIFY” your home. It ended with Bobby Berk urging to:
Smartify yourself, you Smarty Pants you!
The Queer Eye alum spoke with Parade about his favorite smart home devices from Amazon in connection with the SIY/Smartify It Yourself campaign and how they’ve changed his life in multiple ways, some of which are honestly super moving and others that are brilliant for uses you wouldn’t necessarily expect: You can train your Alexa to brew your morning coffee and even to adjust your lighting to help you sleep better at night and feel more energized when you wake up.
spacer
 |
 |
spacer
The etymology and meaning of the following words should open your eyes. Remember, the only thing that matters is the root. Everything else is a cover up, a deception and a LIE.
smart – [ smahrt ] According to Definition.com
noun
-
a sharp local pain, usually superficial, as from a wound, blow, or sting.
-
keen mental suffering, as from wounded feelings, affliction, grievous loss, etc.
-
smarts, Slang. intelligence; common sense
verb (used without object)
-
to be a source of sharp, local, and usually superficial pain, as a wound.
-
to be the cause of a sharp, stinging pain, as an irritating application, a blow, etc.
-
to feel a sharp, stinging pain, as in a wound.
-
to suffer keenly from wounded feelings:
She smarted under their criticism.
-
to feel shame or remorse or to suffer in punishment or in return for something.
verb (used with object)
-
to cause a sharp pain to or in.
Origin and history of smart According to Etymonline
smart(v.)
smart(adj.)
smart(n.)
smarty-pants
smarty-pants
Don’t be such a smarty-pants. You don’t know everything.
OK, smarty-pants, are you going to help me, or just stand there mocking me all night?
smarty-pants
Look, smarty-pants, let’s cut the clowning around.
smart aleck
I know this generation does not believe in TRUTH. They think they can change the meaning of words any time they please. Well, through repitition they can convince people that the meaning has changed but the TRUTH is that it is not. The true meaning may be disguised, covered up, and even erased. That does not CHANGE the TRUTH.
precocious – [ pri-koh-shuhs ]
adjective
-
unusually advanced or mature in development, especially mental development:
a precocious child.
-
prematurely developed, as the mind, faculties, etc.
-
of or relating to premature development.
-
Botany.
-
flowering, fruiting, or ripening early, as plants or fruit.
-
spacer
Movies are full of precocious children, often even declaring them to be precocious as if it were a tremendous attribute. But, children become “precocious” when they are exposed to ADULT ideas and behaviors before they should. They are generally pampered, spoiled and allowed to be have in outrageous ways. They receive attention and recognition for it. People laugh and give signals to the child that they think such behavior is so cute and entertaining.
We are all God’s children.
spacer
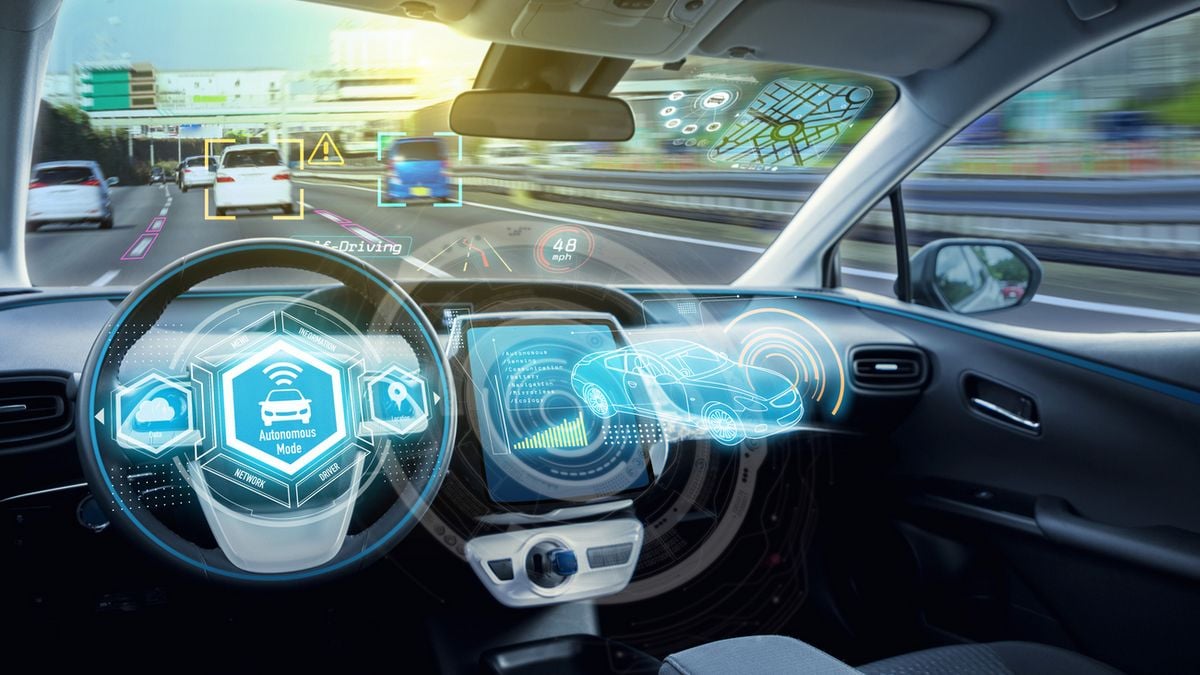

AI Car Features Quick Facts
- Today’s new car models all feature some degree of artificial intelligence.
- Level 3 autonomous driving depends heavily on AI.
- Voice-activated virtual personal assistants can do everything from adjusting the climate control to recommending tourist attractions along your route.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is what all the cool kids are talking about these days, and it’s something to consider when buying a car. Following this year’s Consumer Electronic Show (CES), it’s time we examine AI’s impact on cars and their infotainment systems. Some of the technological advances are positively eye-popping.
We’ll start with a quick review of artificial intelligence, followed by some of the more interesting AI automotive developments and what to expect in the near future. We’ve added jump links so you can skip ahead if you like.
What Is Artificial Intelligence?
According to IBM, AI is technology enabling computers and machines to simulate human learning, comprehension, problem-solving, decision-making, creativity, and autonomy. In other words, AI infuses computers with the power to perform tasks requiring human intelligence through the use of data, algorithms, and adaptive learning.
Can AI Replace Human Intelligence?
Through logic and repetition, AI certainly has the capacity to problem-solve more quickly and reliably than the human brain. However, despite having the capability of learning as it goes, AI can’t duplicate human emotion and imagination.
Is AI Self-Aware?
Presently, AI isn’t self-aware. That is, it doesn’t recognize its place in the world. Will its capacity to learn and evolve ever greater intelligence lead to some sort of consciousness? Most experts assert that AI will restrict itself only to whatever specific tasks it is assigned. To date, no one has figured out how to program emotions or consciousness into a computer.
What Does AI Mean for Cars?
CNET describes the current enthusiasm for artificial intelligence as the “AI Gold Rush,” and it certainly is that. Although we often haven’t affixed the AI label to it, most advanced safety and driver-assistance technologies have ties to AI. Furthermore, the driverless cars of tomorrow will require AI to operate effectively and safely. From voice-activated personal assistants to negotiating busy urban streets without human supervision, AI is totally revolutionizing how we interact with our cars.
Although, primarily because of regulatory entanglements and liability issues, our streets being packed only with driverless vehicles whizzing all about is likely still a decade or more away. Yet, for all intents and purposes, the technology making such a thing possible is mostly developed.
However, there is much more to AI than shouldering the burden of driving the car. AI will be able to not only evaluate your car’s health, delving into the deepest recesses of its systems to sus out current as well as potential problems, but it will also monitor the driver’s health. Moreover, in what is called “contextual technology,” AI will translate repeated driver behavior into personalizing the driver experience. For example, Mercedes-Benz’s MBUX system, which stands for Mercedes-Benz User Experience, can already recognize behavior patterns, using this ability to remind you it’s nearly time to pick up the kids at school or some other repeated routine.
RELATED: Car Safety Features 101: Everything You Need To Know
What Are Software-Defined Vehicles?
As vehicles become more computerized and AI-oriented, the term software-defined vehicles (SDV) is gaining traction. It was a buzzword at this year’s CES. An SDV assumes the characteristics of smartphones, tablets, and other digital devices capable of receiving revisions and refinements via over-the-air (OTA) updates. It has never been more true that today’s cars are rolling computers with software that keeps the wheels turning.
What Are the Coolest New AI Features for 2025
Automotive is a growing category at the annual Customer Electronics Show in Las Vegas, Nevada. This year, three noteworthy AI technologies were highlighted there.
- Omnivision and Philips In-Cabin Vital Signs Monitoring: While Omnivision specializes in digital imaging and touch-and-display technology, Philips concentrates on technologies to promote healthcare innovation. They have collaborated to develop an in-cabin, connected well-being monitoring system. Sensors will measure vital signs like heart rate and breathing rate. Not only does it monitor driver well-being, it can translate that information into climate-control adjustments, audio volume control, cabin lighting, and more.
- Continental Invisible Biometrics Sensing Display: Yep, that Continental, which manufactures and markets tires, is also a leader in technology. Its collaboration with biometric solutions innovator trinamiX has produced an unintrusive wellness monitoring solution. Using a camera and laser projector located behind the dashboard display, it detects passengers through a high-res OLED screen. Not only does it measure a driver’s vital signs, but it maps where each passenger is for more effective employment of airbags while offering other potential benefits.
- Garmin Unified Cabin 2025: What doesn’t Unified Cabin do is the easier question to answer. This technology is a confluence of a variety of cabin electronics–-regardless of brand–-under a single, 6-screen system. Powered by Android, it brings a complete digital experience to four seating positions, which translates into a voice-activated personal assistant for each seat. Moreover, the system will automatically link a phone, earbuds, or other Bluetooth device to whichever seat you choose. A carmaker can tailor Unified Cabin to operate with its electronics.
What Is Honda ASIMO OS?
ASIMO OS is an in-house-developed system that will be the operating system (OS) for Honda’s new O Series electric vehicle (EV) models in 2026. It will bring integrated management across the vehicle’s platform and oversee the electronic control units (ECUs) for systems, including automated driving, driver assistance, and infotainment.
If ASIMO sounds familiar, it was the name of the humanoid robot Honda introduced in 2000 that was capable of walking.
Level 3 Autonomous Driving
Over the next two years, we’ll see a dramatic increase in the availability of Level 3 autonomous driving. Despite claims to the contrary, today’s most advanced-sounding driver-assistance systems, like GM’s Super Cruise, Ford’s BlueCruise, Tesla Autopilot, and others, are Level 2 Autonomous. Level 2 turns the acceleration, steering, and braking control over to the car under certain conditions, but the driver must keep their eyes on the road. You can learn more about the six levels of autonomous driving by reading our article: Self-Driving Cars: Everything You Need To Know.
Level 3 allows you to take both your hands and eyes off the road under certain conditions and at designated speeds. AI makes Level 3 possible. At the beginning of 2025, only Mercedes-Benz markets cars in the United States with Level 3 capability and then only on limited roads in California and Nevada. BMW currently provides its Personal Pilot Level 3 system in some models in Germany but predicts Level 3 in U.S. models in 2025. Honda has had its Sensing Elite Level 3 capability in some of its Honda Legend models in Japan since 2021. However, more carmakers will have Level 3 available on U.S. roadways in the next several months:
- Rivian Autonomy Platform: With a launch date in 2026, this platform will bring hands-free and eyes-off technology to Rivian models.
- Ford BlueCruise: We expect Ford’s BlueCruise to reach Level 3 capability in some 2026 models.
- GM Super Cruise: GM hasn’t predicted when it will upgrade its Super Cruise to Level 3, but we believe it will be no later than 2026 for some models.
- Tesla Autopilot: Tesla claims it already has Level 3 capability but has yet to offer it to the public. Tesla CEO Elon Musk has said there should be at least some limited U.S. availability in 2025.
- Volvo: The carmaker has announced it will offer Level 3 on its 2025 Volvo EX90 electric SUV.
What Is a Large Language Model in a Car?
Although the term may not be familiar, a large language model is the artificial intelligence responsible for crunching mountains of data to understand and generate text as a human does to respond to questions and organize information, including in a car as with Google Assistant. When typing text, the program offers suggestions for completing the sentence, which is a product of its large language model. ChatGPT is a solid example. Large language models constantly evolve, improving their ability to communicate more naturally. We expect that trend to continue, including in vehicles.
How Does Google Assistant Work?
Powered by a large language model, Google Assistant can be found on many car models. For example, it is the virtual personal assistant in the GMC Sierra EV truck. Google Assistant can perform various functions through voice commands, freeing the driver to concentrate on the road. Some of those functions:
- Hands-free phone calling
- Set navigation destinations and obtain real-time traffic updates
- Change climate-control settings
- Set schedule reminders
- Wi-Fi management
- Oversee battery charging
More Engaging AI-Enhanced User Interfaces
AI opens the door to more complex, entertaining, and informative user interfaces. Larger touchscreens, multi-screen displays, and enhanced head-up displays are how we will receive information going forward. Among the newer AI-influenced systems:
- Harman Luna avatar with QVUE: Most of us are familiar with the Harman name for its wide-ranging group of audio companies, including Harman Kardon, JBL, Infinity, and others. However, it is also on the cutting edge of connected car technology. Its range of integrated “Ready” technologies, like Ready Display, Ready Connect, Ready Engage, and Ready Vision QVUE, can turn a car’s cockpit into a beehive of interactive connectivity. It is introducing its Ready Engage “Luna” avatar AI system to function with its A-pillar-to-A-pillar windshield QVUE display and other Ready Vision products. Key features include dynamic street visualization and transparent-hood views.
- Hyundai Mobis Holographic Display: This system employs a specialized film with a holographic optical element to project images and information. It uses the lower portion of the entire windshield from pillar to pillar as its canvas. It’s completely customizable. However, it appears it may not be marketed widely in the United States until 2027.
- BMW Panoramic Vision: Another head-up display involving the entire width of the windshield, this BMW version also utilizes the lower portion of the glass as its screen. BMW hasn’t teased a release date yet, but by 2026 is a safe bet.
AI for Cars Globally
AI isn’t a regional phenomenon; however, AI can develop differently because of local culture and regulations.
European Union
For the American consumer, AI development is focused on easing driver stress and enriching the passenger environment. Although some adaptive cruise control systems provide automatic adjustments to reflect changing speed limits, thus far, adhering to posted speed limits isn’t an AI mandate in this country.
However, in the European Union, maintaining posted speed limits is a core goal of AI driver-assist technology. Intelligent speed assistance (ISA), depending on the ISA system, will issue a warning, apply brake pressure, or reduce engine power when the speed limit is exceeded. In fact, by law, beginning in July 2024, the European Union mandated that manufacturers equip every new car with an ISA system.
China
Unlike the U.S., where each state has its own automotive requirements in addition to federal regulations, China has a single, top-down regulatory structure. Consequently, AI driver-assistance systems are advancing at a somewhat quicker pace there. Carmakers like XPeng and Huawei have developed AI systems that more closely mimic human driving behaviors, exceeding the capabilities of those currently offered in the U.S. market.
4 Tips for Picking a Car Based on AI Capability
One of AI’s attractive features is its transparency. Like the air we breathe, it’s there, but most of us don’t give it much thought. Unless you are a techie, you probably aren’t going to base a car-buying decision on a vehicle’s level of AI proliferation. But if AI proficiency is important to you, we’ve provided some things to look for.
- Driver assist vs. automated driving: How much of the driver’s load do you want AI to shoulder? Most recent model-year vehicles have driver-assistance features like lane-keeping assist and rear cross-traffic alert. Although it’s optional on many models, adaptive cruise control is relatively common, too. These are Level 1 driving aids that may or may not be AI-enhanced. However, if you want a greater degree of automation, you’ll need a Level 2 or Level 3 system. As already described, Level 2 allows removing your hands from the wheel under certain conditions, while Level 3 also allows you to take your eyes off the road in certain situations.
- Voice-activated assistants: In-car personal assistants are now quite common in new models. Whether it’s “Hey, Alexa” with Alexa Auto, ChatGPT as with “Hey, Mercedes” in that carmaker’s MBUX OS, or the virtual assistant from some other system, they are a form of human-machine interactions. These assistants come with varying degrees of sophistication. The level of responsiveness, capability to understand, and capacity to learn your preferences aren’t the same from one system to the next. Some extra research, as well as testing the personal assistant during the test drive is required to make the right pick for you.
- Over-the-air (OTA) updates: Technology doesn’t stand still. You want to ensure that whichever system a vehicle features that said system can update in real-time over the air.
- Extra costs: Be sure you understand what an AI operating system is capable of as is and what requires a subscription. Any subscription cost must be factored into your budget.
RELATED: Adaptive Cruise Control: How Does It Work?
Our Take
AI-enhanced car technology is advancing at a blistering pace. It has the potential to make driving less stressful, safer, and more entertaining. It’s probably capable of things we have yet to realize. However, we’ve reached the point at which it’s no longer whether a new model car features AI but how much AI it has.
Next-gen US trains to go blazing at 160 mph, replacing 25-year-old fleet
The NextGen Acela trains will boost seating capacity by 25%, accommodating 386 passengers with additional features like USB ports and contactless restrooms.

The new trains are being built by Alstom, a global leader in rail manufacturing. Amtrak’s expertise as the only high-speed rail operator in the U.S., combined with Alstom’s proven track record, has resulted in the NextGen Acela.
This collaboration is part of a $2.45 billion investment to modernize the heavily traveled Northeast Corridor (NEC).
Rail enthusiasts have already spotted the new Acela trains in action. YouTube user Fan Railer shared footage of the NextGen Acela reaching speeds of 165 mph during a test run through Wickford Junction. These tests are crucial to ensuring the trains meet safety and performance standards before entering regular service.
Originally planned for release nearly four years ago, the new Acela trains faced setbacks due to manufacturing challenges and the pandemic. A federal watchdog report even flagged defects in some trainsets, further delaying the launch. However, Amtrak has resolved these issues, and the trains are now in the final stretch before public rollout.
Amtrak has confirmed that the new Acela trains will enter service in spring 2025. The modernized fleet promises to enhance the travel experience for millions of passengers along the NEC, bringing better connectivity, efficiency, and sustainability. The wait is almost over, and the future of American high-speed rail is finally coming into view.
spacer
Exploring the Smart Trains and Connected Railway
Today, the integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming railways, creating smart trains and connected railway systems. These innovations enable real-time data exchange between trains, tracks, and control centres, enhancing operational efficiency, safety, and passenger experience.
This article will explore the potential of smart trains to transform mobility within the railway sector while creating a more connected ecosystem that enhances efficiency, safety, and passenger experience.
SMART Trains
Smart trains are developed through the integration of advanced embedded systems, onboard sensors, and communication modules that facilitate real-time data collection, transmission, and analysis. These sensors monitor critical train components, including wheel temperature, vibration levels, engine performance, and braking systems. The data collected is relayed to a central control centre, enabling continuous assessment and optimisation of operational parameters.

Future of IoT in Railways
IoT is setting up the ground for autonomous trains where AI-driven systems handle driving, monitoring, and safety operations without human intervention.
AI and Machine Learning will be integral to advanced predictive maintenance, enabling rail operators to forecast component failures months in advance with greater accuracy.
The advancement of smart trains outlines a meaningful enhancement in operational efficiency, safety, and passenger experience within the railway industry. The incorporation of technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and 5G connectivity is creating a more responsive railway ecosystem. Smart coaches in Indian Railways, equipped with sensors for real-time diagnostics and passenger information systems, demonstrate practical implementations of these developments. While challenges such as the higher costs of implementing these technologies and integration with existing systems persist, advancements like Maglev and Hyperloop hold the potential to further enhance rail travel by offering faster and more efficient transportation alternatives.
spacer
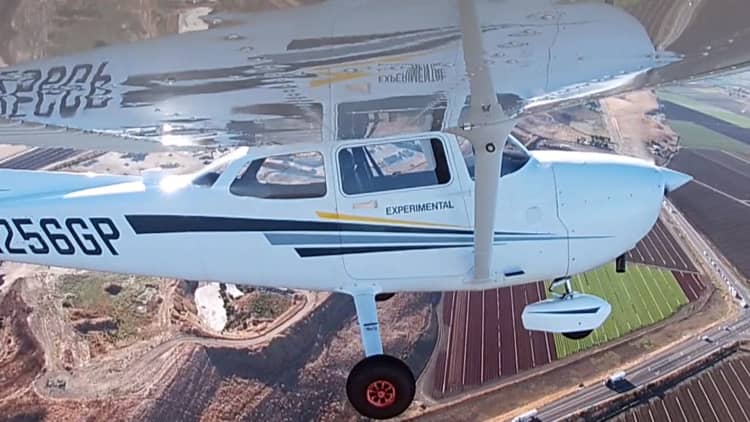
Reliable Robotics and Xwing are two Bay Area start-ups working on planes that can fly themselves — no pilot required. Rather than building new aircraft, both companies have retrofitted Cessna Grand Caravans. The planes can fly autonomously while a remote operator monitors the flight, taking control if needed.
Both companies said they are working with major logistics companies to deliver cargo as a first use case once FAA approval happens.
Xwing took CNBC up for a test flight where the pilot didn’t touch the controls once. Watch the video to see how the technology works and learn when self-flying planes could become the norm.
Forbes Staff.
Suzanne Rowan Kelleher covers travel for Forbes.
The aircraft are already here. Pilot unions are preparing for battle. And the FAA is playing it cool. Autonomous flight is coming to civil aviation sooner than anyone thinks, and it may prove to be a surprising boon for flyover country.
InJanuary, Boeing CEO Dave Calhoun revealed an open secret in the world of aviation. “I think the future of autonomy is real for civil,” he told Bloomberg TV, before quickly offering some qualifiers. “It’s going to take time. Everyone’s got to build confidence. We need a certification process that we all have faith and believe in.”
The U.S. military has been flying autonomous planes for decades, of course, but always in a segregated airspace. Now it’s becoming increasingly clear that self-flying planes are coming to commercial aviation, and not in some distant Jetsons future world. Aircraft manufacturers are working toward it. Airlines are eager for it. The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) is preparing for it. And pilot unions acknowledge the threat is looming on the horizon.
A decade ago, the conversation was largely speculative. But today, many in the aviation industry believe that small, self-flying planes could be carrying passengers by the end of this decade. Then, barring no major safety incidents, it could take as little as another decade before larger passenger jets operate without a pilot on the flight deck.
“It’s all about money,” says Dennis Tajer, a pilot for 35 years and the spokesman for Allied Pilots Association, which represents 15,000 American Airlines pilots. “Manufacturers are looking for the next innovative technology to deploy so that they can sell it and make money, and airlines are looking at how they can do this more cheaply.”
It’s a charge that’s difficult to rebut. Six years ago, a report from the Swiss bank UBS estimated that autonomous planes could save the air transportation industry more than $35 billion per year. Still, the same report flagged a bright red public perception problem. A 2017 global survey found that a majority of people would be unwilling to fly in a plane without a pilot, even if the airfare were cheaper. The next year, a public survey from Ipsos found that 81% of Americans would not be comfortable traveling on a self-flying plane. Notably, that survey was sponsored by the Air Lines Pilots Association (ALPA), whose 65,000 members make up the largest pilot union in the country.
The introduction of autonomous aircraft into the civil aviation mix will begin with small cargo planes, led by companies like Xwing, a Northern California-based startup. “We took an existing Cessna airframe,” says Xwing CEO Marc Piette, “which is the most widely used express cargo airframe, and we’ve been modifying that vehicle to convert it to a remotely-supervised vehicle. We think the cargo market is the best first place to deploy this. And we’ve been very deliberate.”
For the past few years, Xwing has been running automated test missions, mainly in California. A flight plan is submitted, just as if there were a human pilot, and the flight’s parameters are pre-programmed before takeoff. “It’s really a one-click thing,” Piette says. “You engage the system and it runs its mission.”
Until the technology is certified by the FAA, however, there will need to be a safety pilot on board. This allows Xwing to fly without jumping through regulatory hoops. “The safety pilot can disconnect a system and revert the aircraft to manual flying, but otherwise doesn’t do anything but monitor the system. It’s a very boring job,” Piette explains. Meanwhile, the Cessna is operated from the ground, with one human controller watching a moving map on a screen and interfacing with air traffic control.
“All of these companies are really looking forward to the day where there will not be a pilot on board.”
Once the technology is certified, Xwing plans to introduce and operate these vehicles by late 2025 and then make it available to other operators. “To give you an example, FedEx has about 240 Cessna 208s for its U.S. network,” Piette says, alluding to the scalability of the venture. He expects his autonomous aircraft to be transporting human passengers by the end of this decade.
In a local power outage, you can have your wireless internet at home with a simple battery backup to your modem and wireless router. However, in a wide power blackout, where your internet provider has no power, you will lose your internet connection even if your modem and router are powered. Internet services are often still functional during a power outage, provided you have an alternative power source for your internet equipment. Wi-Fi routers need a power source to function, meaning Wi-Fi cannot work without electricity. There are various methods to access the internet during a power outage, including backup power sources, and mobile hotspots.
 In this video, we’re exploring products that smarten up our family life and could help yours, too:
In this video, we’re exploring products that smarten up our family life and could help yours, too:  As we embrace the future, investing in smart products is essential for a convenient and modern home. Don’t miss out on the opportunity to upgrade your living space with these innovative solutions.
As we embrace the future, investing in smart products is essential for a convenient and modern home. Don’t miss out on the opportunity to upgrade your living space with these innovative solutions.  If you enjoyed this video, don’t forget to hit the like button, subscribe, and ring the bell for notifications. Stay tuned for more tips and insights on making your home smarter and your life easier!
If you enjoyed this video, don’t forget to hit the like button, subscribe, and ring the bell for notifications. Stay tuned for more tips and insights on making your home smarter and your life easier! 





















 Subscribe:
Subscribe: 
